E-Invoicing Application
Introduction
This was my first UNSW software engineering work shop project, a SaaS e-invoicing app, includes features such as invoice creation, validation, rendering and sending.The project is deployed on AWS, it uses UBL-XML messaging over the PEPPOL network and aimed at meeting SME requirements in a standards-compliant way.
- E-Invoicing ?
- Australia is shifting from paper and emailed PDFs to structured, machine-readable invoices that move directly between accounting systems. NSW accelerated the change by mandating that all state agencies accept e-invoices for goods and services up to AUD 1 million from 2022. The switch, part of the broader Industry 4.0 push, delivers faster payments, fewer errors, and tighter fraud controls.
Team
Our four-person team adopted clear roles: Team Leader, Product Owner (myself), and Delivery Manager. As Product Owner, I shaped the product vision, prioritised the backlog, and kept the team focused on the highest-value features. We ran the project with an Agile cadence: weekly sprint meetings plus asynchronous check-ins, tracking work in Jira and storing documentation in Confluence.
Requirements Engineering
Before coding began, we carried out a full requirements-engineering phase: reviewing the A-NZ PEPPOL interoperability rules, mapping user stories with clear acceptance criteria, and documenting both functional and non-functional requirements.
We studied into the AU/NZ UBL implementation guides and PEPPOL specifications (PEPPOL specifiations), turning requirements into concrete backlog items from day one.
Application Architecture
-
Deployment Layer
The deployment layer is responsible for deploying the application to a cloud provider. The application is deployed on Amazon’s Web Service (AWS) Elastic Beanstalk. It provides an environment that automatically handles the deployment, scaling, and load balancing of the application. It is a scalable, reliable, and cost-effective solution for deploying web applications.
-
Interface Layer
The interface layer is responsible for providing a user-friendly interface for users to interact with the application. The application uses a web-based user interface through HTML, CSS, and Javascript. The frontend framework used React, which provides reusable components and robust state management, connecting to the backend via RESTful APIs. The frontend is deployed on AWS Amplify.
-
Service Layer
The service layer is responsible for providing the backend functionality of the application. We create a RESTful API using Flask, which is a lightweight and efficient Python web framework that provides necessary tools. The API will provide endpoints and routes for creating an invoice, here is a example of our creation API on Swagger
System Modelling
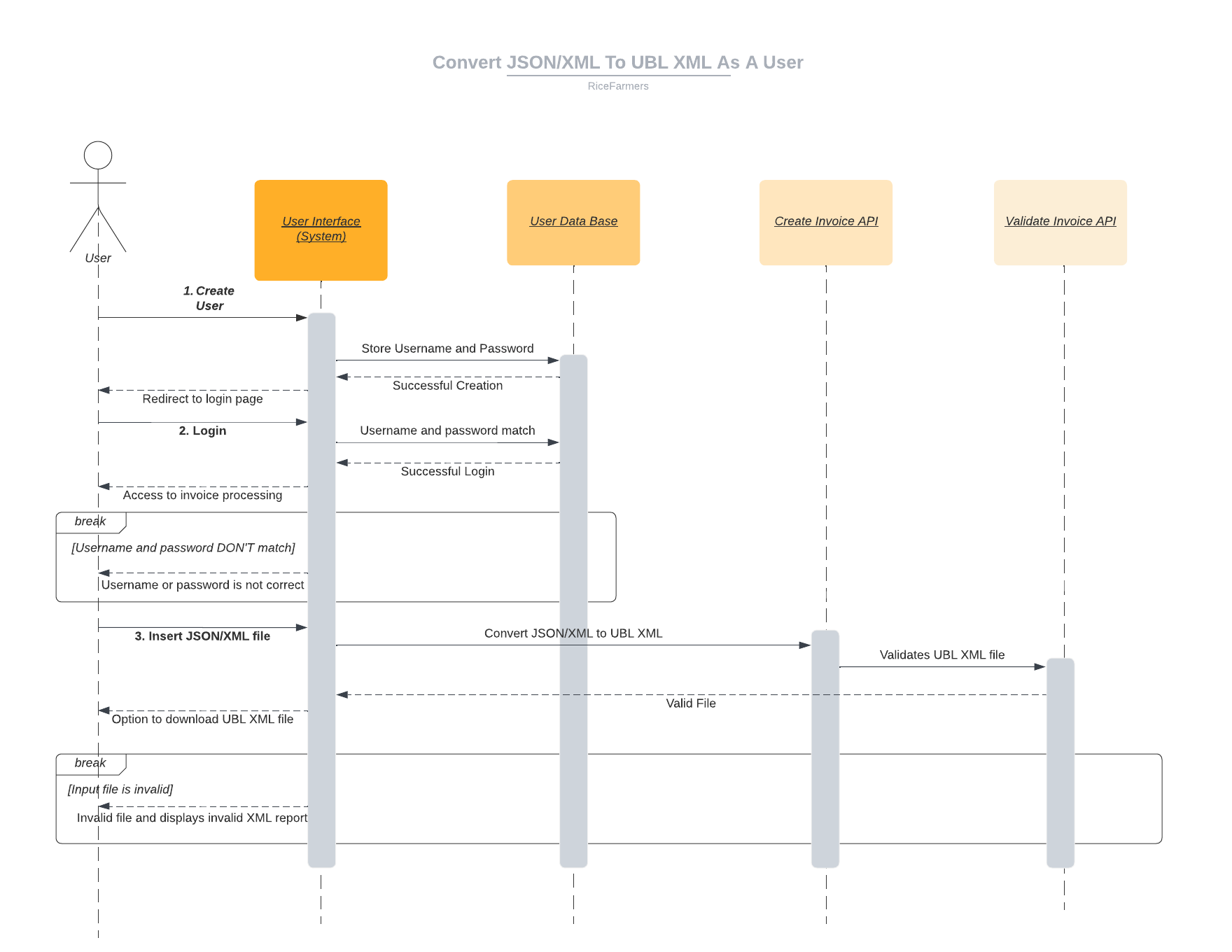 We modelled the application with UML sequence diagrams that trace the complete user journey, from sign-up and authentication through file upload, JSON/XML-to-UBL conversion, validation, and download. The diagram spans the user interface, user database, and two micro-service APIs. Mapping each call and break branch upfront helped clarify service boundaries, data transformations, and error handling, giving the team a shared blueprint before any code was written.
We modelled the application with UML sequence diagrams that trace the complete user journey, from sign-up and authentication through file upload, JSON/XML-to-UBL conversion, validation, and download. The diagram spans the user interface, user database, and two micro-service APIs. Mapping each call and break branch upfront helped clarify service boundaries, data transformations, and error handling, giving the team a shared blueprint before any code was written.
Develop
Backend
The hardest challenge was the invoice-creation engine: we had to parse four input formats (xml, csv, xls, json) using different libraries, normalise them into one consistent XML tree, and then map that tree onto the PEPPOL-compliant UBL schema.
To guarantee UBL compliance, each raw input is first transformed into a single canonical JSON representation. From that JSON we generate a fresh XML document that exactly matches the PEPPOL UBL schema. Thus, we used thirdparty library for each format to help us for the normalisation.
import csv
import openpyxl
import json
import xmltodict
CSV to json example:
def csv_to_json(file_path):
data = []
with open(file_path) as csv_file:
csv_reader = csv.DictReader(csv_file)
for row in csv_reader:
record = {}
for key, value in row.items():
parts = key.split('/')
current_dict = record
for part in parts[:-1]:
current_dict.setdefault(part, {})
current_dict = current_dict[part]
current_dict[parts[-1]] = str(value)
data.append(record)
write_file(CONVERT_FILE, json.dumps(data[0], indent=2))
Frontend
The UI is a React single-page application styled with Bootstrap 5. Bootstrap’s grid and utility classes give us responsive layouts with minimal custom CSS, while React components handle data exchange with the backend through REST calls and display consistent loading, error, and success states.
We enhanced the interface with an AI assistant: the React client calls the ChatGPT API so users can generate a UBL-compliant invoice skeleton from plain-language prompts and request on-the-fly edits to their XML before submission.
We supplied the AI with a fixed system prompt that spells out the UBL schema, and formatting rules, so every response either produces a valid invoice skeleton or returns a well-formed XML patch the user can merge directly.
const systemMessage = {
role: "system",
content: "Only help the user to create the UBL XML, you should by default create invoice unless the client wants you to create other.\
When generating UBL XML put ``` around the code, we will use ``` as sperator and turn the string inside ``` to a file for rendering\
Make sure the UBL type is invoice \
it should follow this format: \
<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\"?> \
<Invoice xmlns:cac=\"urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:schema:xsd:CommonAggregateComponents-2\" xmlns:cbc=\"urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:schema:xsd:CommonBasicComponents-2\" xmlns=\"urn:oasis:names:specification:ubl:schema:xsd:Invoice-2\"> \
</Invoice> \
"
}
Call the OpenAI API for completions.
await fetch("https://api.openai.com/v1/chat/completions", {
method: "POST",
headers: {
"Authorization": "Bearer " + API_KEY,
"Content-Type": "application/json"
},
body: JSON.stringify(requestBody)
})
.then((data) => {
return data.json()
})
.then((data) => {
console.log(data);
console.log(data.choices[0].message.content)
setMessages(
[...chatMessages, {
message: data.choices[0].message.content,
sender: "ChatGPT"
}]
);
getXML(data.choices[0].message.content);
setTyping(false);
})
}
Deployment
| Layer | Platform | Duty |
|---|---|---|
| Backend | AWS Elastic Beanstalk | Flask REST APIs, including authentication and token management |
| Frontend | AWS Amplify | React single-page app |