messenger
Introduction
The application is implemented in Java (OpenJDK 11.0.21) using a client-server architecture. It consists of one central server and multiple clients. Text messages are transmitted over TCP, while video content is sent directly between clients using UDP.
Design
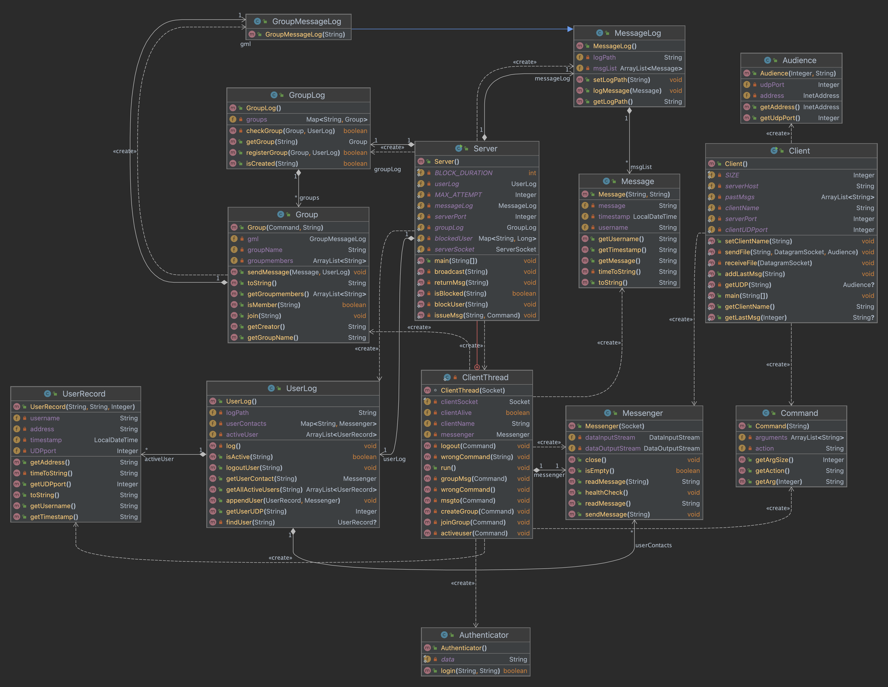
Files:
Audience.java- Encapsulate the UDP port and user addresss
Authenticator.java- Helps to authenticate the user by reading credentials.txt
Client.java- Client application, communicate with the server
Command.java- Helps to process the user’s command (e.g.: /activeuser, /msgto, /logout … etc)
Group.java- A group object helps to manage the group mechanism of the application
GroupLog.java- Helps to manage all the groups created in the application
GroupMessageLog.java- Extends the MessageLog.java class, helps with the messages in a group
Message.java- Helps with processing messages, contains the sender’s name (on group chat) or receive name (on private message), also a timestamp
MessageLog.java- Help with logging messages sent in server in file.
Messenger.java- Help with sending and receiving messages between server and client. Encapsulate the
DataInputStreamandDataOutputStreamand provides more features
- Help with sending and receiving messages between server and client. Encapsulate the
Server.java- Server application, communicate with multiple clients.
UserLog.java- Help with managing all users’ activities and log them in
userlog.txt
- Help with managing all users’ activities and log them in
UserRecord.java- Help with managing the user’s basic information
The application requires a credential.txt file to store all the user and their password. The application on run will generate extra files, such as group message log file. The application will automatically update content of the log files (userlog.txt, messagelog.txt, and group message log file)
Application Layer Message Format
Messages are conveyed as Command objects; during communication, the client sends plain text, and the server reads and parses it into a Command object.
The Command object comprises an action and arguments. The action represents one of the provided commands. The server takes an action and then executes the corresponding command by interpreting the subsequent arguments.
In more detail, when the client sends a message to execute a command, the message is split into words using the space character as the delimiter. The first word denotes the action, and the subsequent words are the arguments. If the action is not one of the provided commands, the server promptly informs the client that the command is invalid.
System Functionality
Sever:
$ java Server 8000 3
On running, server listen to every new connect and create a thread for it.
Client:
$ java Client localhost 8000 64
On running, client establish a TCP connect to the server with the given address. Client creates two threads:
- One thread to display all incoming response from the server.
- One thread waiting for any incoming UDP files.
P2P: The client-side implementation of the p2pvideo command assumes that the client has previously executed the /activeuser command. When invoked, the client uses its UDP socket to transmit the source file in packet-sized chunks. The first packet includes metadata such as the sender’s identity and the filename, while the final packet is an empty packet indicating the end of the transfer. Notably, the server is unaware of the p2pvideo command and remains uninvolved throughout the entire process.
Sender:
Please enter your command:
/p2pvideo joe example.mp4
127.0.0.1
example.mp4 has been uploaded
/msgto /activeuser /creategroup /joingroup / groupmsg /logout /p2pvideo
Please enter your command:
Receiver:
/msgto /activeuser /creategroup /joingroup / groupmsg /logout /p2pvideo
Please enter your command:
Received file 'example.mp4' from: xi
/msgto /activeuser /creategroup /joingroup / groupmsg /logout /p2pvideo
Please enter your command:
UML Diagram